I - What is an organization?
1/ Distinction between individual and collective action.
COLLECTIVE ACTION
It is the behaviour or action of a group working towards a common goal.
The strength, knowledge and efforts of the group are combined to reach a goal.
INDIVIDUAL ACTION:
One person pursues a goal on its own .
Collective action is usually more effective than individual action
Think about two examples of a collective action and of an individual action and share with your team mates. Write down your ideas and then share with another team. Complete their list.
2/ From collective action to organization
When a group wants to act over the long term, it chooses a legal framework adapted to its activity and its purpose. Then the organization can get subventions, buy and sell goods, make contracts with suppliers and services providers.
To exist an organization needs 5 criteria:
A group of individuals - A common goal - A distribution and coordination of tasks - The group has to last in time - An adapted legal framework
Think about an organization you know and define the 5 criteria it has.
3/ How does an organization work?
A/ Distribution and coordination of tasks
When a group wants to reach a common goal, it is necessary to distribute and coordinate tasks among its members. It allows the group to be more efficient in order to reach the common goal.
B/ Resources of an organization
In order to reach the common objective, the organization sets up resources:
Human resources - Financial resources - Material resources - Immaterial resources
C/ Information flow and decision making
Decision making is a process to make choices among different possible actions considering the information available.
The organization has to decide who makes decisions and how.
D/ Distribution of power
It can be:
Central: given to a limited number of members
or
Decentralized: shared between all members.

II - The various types of organizations
1 - With the words below, fill in the gaps :
bank/help/private/profit/donations/ make profit/ investors/government/taxes/individuals/benefit/trustees.
Private sector organisations are owned by ________. These businesses are driven by __________. The profit from___________ sector organisations benefits the owners, shareholders and __________. They are financed by private money from shareholders and by _________ loans. Public sector organisations are owned by the _______________. They provide goods and services for the _______________ of the community. They are run by the government. They operate with money raised from _______________.
Civil society organisations are owned and run voluntarily by ________________. These organisations are not run by the need to ______________ but by the need to _____________ the community. They operate with money from ___________ and gifts. Any profits are reinvested in the organisation.
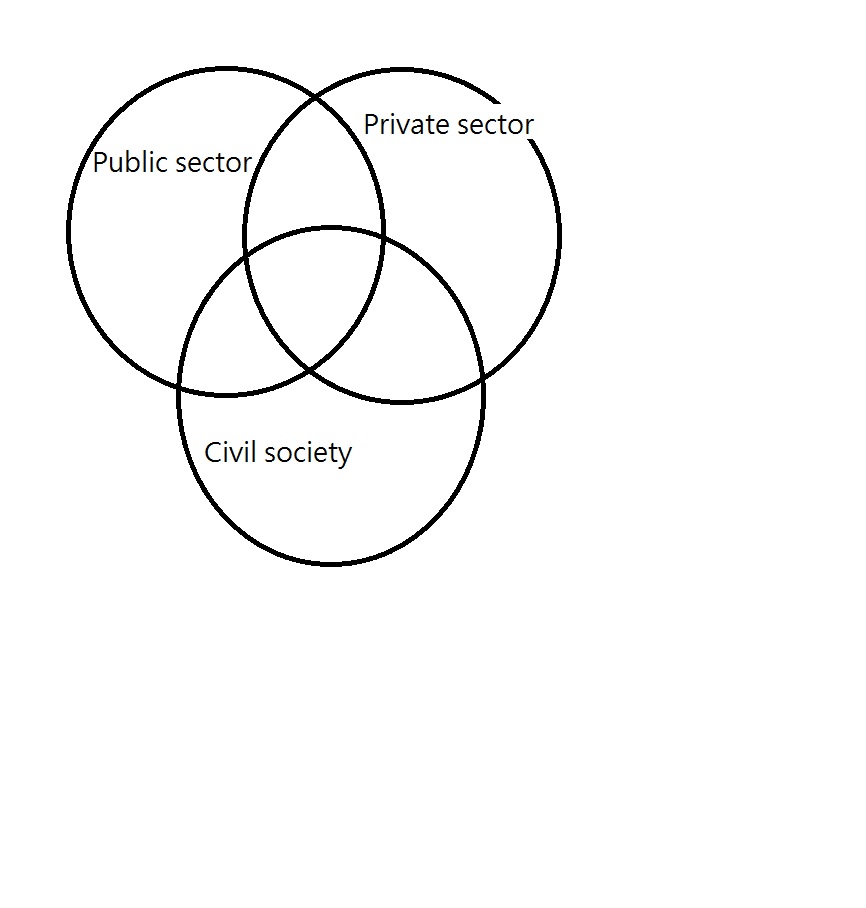
2 / Draw a diagram to place the logos in the right circle :
For each of the logos, determine whether the organisation they represent is part of the private sector, the public sector or the civil society sector and place them at the right place.












3/ Present an organization :
A - Examples
APPLE
Apple Computers, Inc. was founded on April 1, 1976, by college dropouts Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, who brought to the new company a vision of changing the way people viewed computers. Jobs and Wozniak wanted to make computers small enough for people to have them in their homes or offices. Simply put, they wanted a computer that was user-friendly.
Jobs and Wozniak started out building the Apple I in Jobs' garage and sold them without a monitor, keyboard, or casing (which they decided to add on in 1977). The Apple II revolutionized the computer industry with the introduction of the first-ever color graphics.1 Sales jumped from $7.8 million in 1978 to $117 million in 1980, the year Apple went public.
https://www.loc.gov/rr/business/businesshistory/April/apple.html#targetText=Company%20History,in%20their%20homes%20or%20offices.
FEEDING AMERICA
The concept of food banking was developed by John van Hengel in Phoenix, AZ in the late 1960s. Van Hengel, a retired businessman, had been volunteering at a soup kitchen trying to find food to serve the hungry. (…)
Van Hengel established St. Mary's Food Bank in Phoenix, AZ as the nation's first food bank. In its initial year, van Hengel and his team of volunteers distributed 275,000 pounds of food to people in need. Word of the food bank's success quickly spread, and states began to take note. By 1977, food banks had been established in 18 cities across the country.
In 1978, as the number of food banks began to increase, van Hengel created a national organization for food banks and in 1979 he established Second Harvest, which was later called America's Second Harvest the Nation's Food Bank Network. In 2008, the network changed its name to Feeding America to better reflect the mission of the organization.
Today, Feeding America is the nation's largest domestic hunger-relief organization—a powerful and efficient network of 200 food banks across the country. (…) We feed 46 million people at risk of hunger, including 12 million children and 7 million seniors.
For each of these organizations find out their characteritics such as : type, examples of actions, type of activity, sector of activity, size, nationality, location, scope.
4/ Characteristics of an organization
There are various types of organizations. They can be identified thanks to essential characteristics:
Goal/ Purpose - Profit - Type of activity - Type of organization- Legal status - Resources 7-Distribution of power - Geographical scope (field)
Goal/ Purpose: It corresponds to the longer-term orientation of the activity of the organization, it is the fundamental purpose. It can be economic, cultural, social, sportive or humanitarian. An organization can have more than one purpose.
Profit: An organization can be:
For profit: usually private companies ex: Apple
Non-profit: it can share a leisure, humanitarian role ex: Greenpeace
Nature of activity: it can be the production of goods or service delivery.
Types: Company (private and for profit) - non-profit organizations (ex: Greenpeace) or public corporations (organizations) ex: libraries, schools, healthcare.
Legal status: Rights and duties of the organization depends on its legal capacity determined by its legal status ex: declared organizations or limited company.
Resources: Human, financial, material, immaterial.
Distribution of power: Centralized or decentralized.
- Geographical scope/ field: It corresponds to the field of intervention. It can be local, regional, national or international.
B - Complete this document :
C - With your team mates, draw a poster to recap what you have learnt in this lesson and display it in the classroom.
D - Your team has been given an organization to describe to the others. You have to perform your speech in front of the class using a power point document.
III - TEST
You have to learn the vocabulary and the definitions.
Be sure you have understood the lesson.
It is still time to ask for help!